Kubernetes CRD
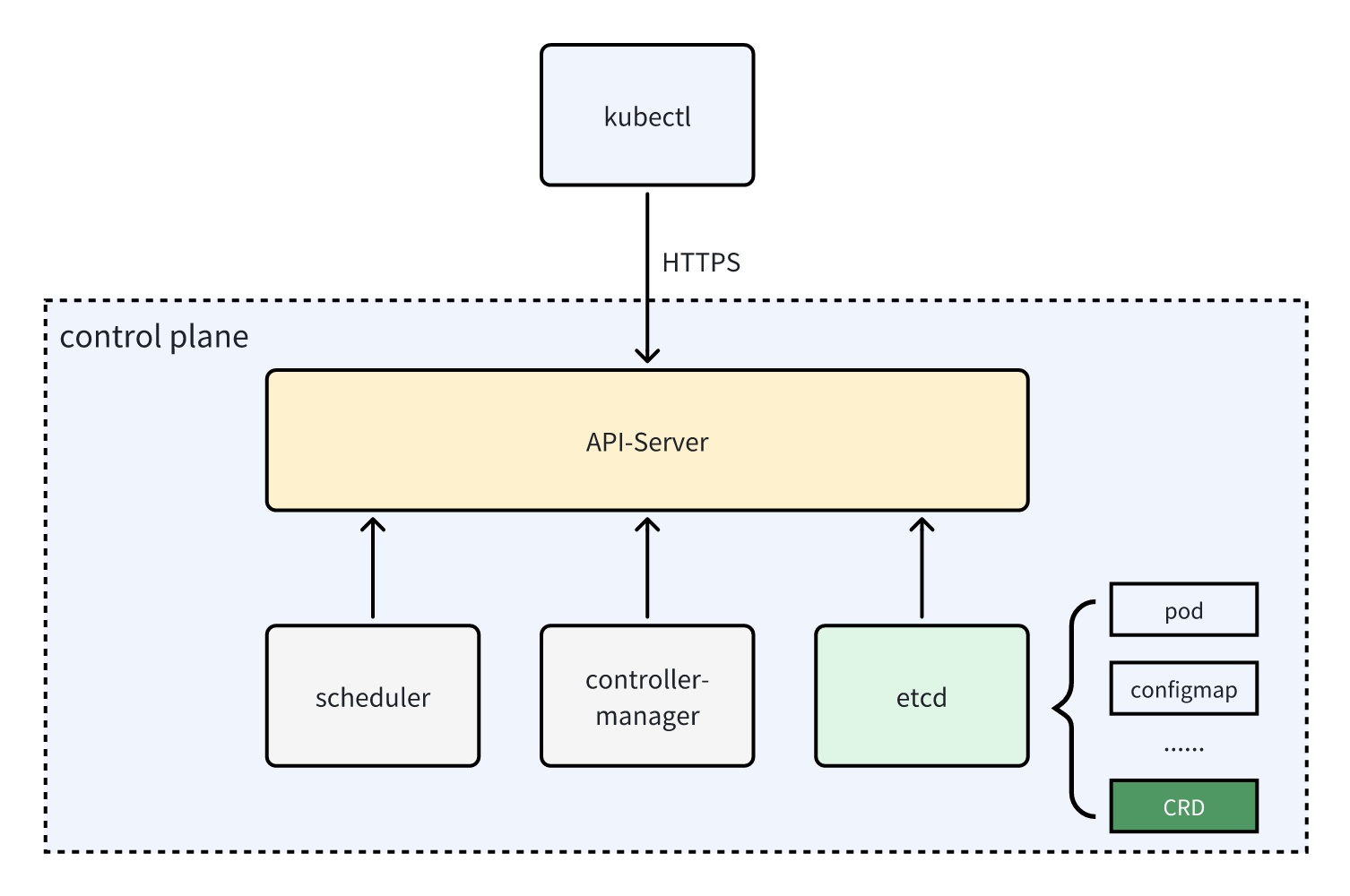
在 kubernetes 中有一系列内置的资源,诸如:pod、deployment、configmap、service …… 等等,它们由 k8s 的内部组件管理。而除了这些内置资源之外,k8s 还提供了另外一种方式让用户可以随意地自定义资源,这就是 CRD (全称 CustomResourceDefinitions) 。
例如,我可以通过 CRD 去定义一个 mypod、myjob、myanything 等等资源,一旦注册成功,那么这些自定义资源便会享受与内置资源相同的待遇。具体而言就是:
- 我们可以像使用
kubectl 增删改查 deployment 一样去操作这些 CRD 自定义资源。
CRD 自定义资源的数据跟 pod 等内置资源一样会存储到 k8s 控制平面的 etcd 中。
需要注意的是,CRD 在不同的语境下有不同的含义,有时候可能只是指 k8s 中的 CustomResourceDefinitions 这一种特定的资源,有时候也可能是指用户通过 CRD 所创建出来的自定义资源。
狭义上的 CRD (全称 CustomResourceDefinitions) 是 k8s 中的一种特殊的内置资源,我们可以通过它去创建我们自定义的其它资源。例如,我们可以通过 CRD 去创建一个叫 CronTab 的资源:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
# 名称必须匹配 <plural>.<group>
name: crontabs.stable.example.com
spec:
# group 名称,用于 REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
group: stable.example.com
versions:
- name: v1
served: true
storage: true
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
type: object
properties:
# 定义属性
spec:
type: object
properties:
cronSpec:
type: string
image:
type: string
# 作用范围可以是 Namespaced 或者 Cluster
scope: Namespaced
names:
# 复数名称,使用于 URL: /apis/<group>/<version>/<plural>
plural: crontabs
# 单数名称,可用于 CLI
singular: crontab
# 驼峰单数,用于资源清单
kind: CronTab
# 名字简写,可用于 CLI
shortNames:
- ct
|
一旦我们 apply 这个 yaml 文件,那么我们的自定义资源 CronTab 也就注册到 k8s 了。这个时候我们就可以任意操作这个自定义资源,比如 my-crontab.yaml:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: "stable.example.com/v1"
kind: CronTab
metadata:
name: my-new-cron-object
spec:
cronSpec: "* * * * */5"
image: my-awesome-cron-image
|
执行 kubectl apply -f my-crontab.yaml 就可以创建我们自定义的 CronTab,执行 kubectl get crontab 就可以查询到我们自定义的 CronTab 列表。

通过 CRD 自定义资源的优点是,我们无需操心自定义资源的数据存储,也无需再额外实现一个 http server 去对外暴露操作这些自定义资源的 API 接口,因为这些 k8s 都帮我们做好了,我们只需要像其它内置资源一样使用自定义资源即可。
但是!只有 CRD 往往是不够的,例如上文中我们执行 kubectl apply -f my-crontab.yaml 创建了一个 crontab 自定义资源,但是这个 crontab 不会有任何执行的内容(不会跑任何程序),而很多场景下我们是希望自定义资源能够执行点什么。这个时候我们就需要 Operator 了。
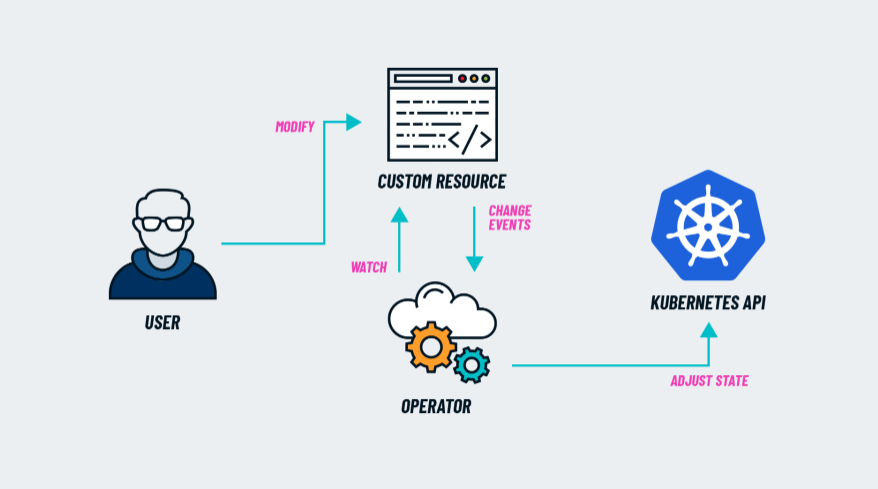
Operator
Operator 其实就是 custom resource controller(自定义资源的控制器),它干的事情就是监听自定义资源的变更,然后针对性地做一些操作。例如,监听到某个自定义资源被创建后,Operator 可以读取这个自定义资源的属性然后创建一个 pod 去运行具体的程序,并将这个 pod 绑定到自定义资源对象上。

那 Operator 以何种方式存在呢?其实它跟普通的服务一样,可以是 deployment,也可以是 statefuleSet。
至于常说的 Operator pattern 其实就是 CRD + custom controller 这种模式。
Kubebuilder
我们在构建项目时常常希望有一个好用的框架,能够提供一系列工具帮助开发者更轻松地进行创建、测试和部署。而针对 CRD 和 Operator 的场景就有这么一个框架 Kubebuilder。
接下来我将会使用 Kubebuilder 创建一个小项目,其中会创建一个自定义资源 Foo ,并在 controller 中监听这个资源的变更并把它打印出来。
1. 安装
1
2
3
|
# download kubebuilder and install locally.
curl -L -o kubebuilder "https://go.kubebuilder.io/dl/latest/$(go env GOOS)/$(go env GOARCH)"
chmod +x kubebuilder && mv kubebuilder /usr/local/bin/
|
2. 创建一个测试目录
1
2
|
mkdir kubebuilder-test
cd kubebuilder-test
|
3. 初始化项目
1
|
kubebuilder init --domain mytest.domain --repo mytest.domain/foo
|
4. 定义 CRD
假设我们想要定义一个如下格式的 CRD:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: "mygroup.mytest.domain/v1"
kind: Foo
metadata:
name: xxx
spec:
image: image
msg: message
|
那么我们需要创建一个 CRD(本质上也是创建一个 API ):
1
|
kubebuilder create api --group mygroup --version v1 --kind Foo
|
执行之后输入 y 确认生成,然后 kubebuilder 会帮我们自动创建一些目录和文件,其中:
api/v1/foo_types.go 文件中定义了这个 CRD(也是 API)。internal/controllers/foo_controller.go 文件则是控制 CRD 的业务逻辑。
由于自动生成的文件只是一个基本框架,我们需要按照自己的需求进行相应的修改。
a. 在代码中修改 CRD 的结构
首先,修改 api/v1/foo_types.go 调整 CRD 的结构(注意不要删除 //+kubebuilder 这种注释):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// FooSpec defines the desired state of Foo
type FooSpec struct {
Image string `json:"image"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
// FooStatus defines the observed state of Foo
type FooStatus struct {
PodName string `json:"podName"`
}
|
b. 通过命令自动生成 CRD yaml
执行 make manifests 命令之后,kubebuilder 就会在 config/crd/bases 目录下生成一个 mygroup.mytest.domain_foos.yaml 文件,这个文件就是我们定义 CRD 的 yaml 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
annotations:
controller-gen.kubebuilder.io/version: v0.13.0
name: foos.mygroup.mytest.domain
spec:
group: mygroup.mytest.domain
names:
kind: Foo
listKind: FooList
plural: foos
singular: foo
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: Foo is the Schema for the foos API
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: FooSpec defines the desired state of Foo
properties:
image:
type: string
msg:
type: string
required:
- image
- msg
type: object
status:
description: FooStatus defines the observed state of Foo
properties:
podName:
type: string
required:
- podName
type: object
type: object
served: true
storage: true
subresources:
status: {}
|
make manifests 指令执行的具体内容定义在了 Makefile 文件中:
1
2
3
|
.PHONY: manifests
manifests: controller-gen ## Generate WebhookConfiguration, ClusterRole and CustomResourceDefinition objects.
$(CONTROLLER_GEN) rbac:roleName=manager-role crd webhook paths="./..." output:crd:artifacts:config=config/crd/bases
|
从中可以看到其实 kubebuilder 使用了 controller-gen 工具去扫描代码中特定格式的注释(如 //+kubebuilder:...)进而生成的 CRD yaml 文件。
5. 补充 controller 逻辑
假设我们要监听用户创建的自定义资源 Foo 然后把它的属性打印出来。
a. 修改 controller 补充业务逻辑
修改 internal/controllers/foo_controller.go 文件补充我们自己的业务逻辑,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
func (r *FooReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {
l := log.FromContext(ctx)
// 补充业务逻辑
foo := &mygroupv1.Foo{}
if err := r.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, foo); err != nil {
l.Error(err, "unable to fetch Foo")
return ctrl.Result{}, client.IgnoreNotFound(err)
}
// 打印 Foo 属性
l.Info("Received Foo", "Image", foo.Spec.Image, "Msg", foo.Spec.Msg)
return ctrl.Result{}, nil
}
// SetupWithManager sets up the controller with the Manager.
func (r *FooReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
For(&mygroupv1.Foo{}).
Complete(r)
}
|
b. 进行测试
注意:测试需要有本地或远程的 k8s 集群环境,其将会默认使用跟当前 kubectl 一致的环境。
执行 make install 注册 CRD ,从 Makefile 中可以看到其实际执行了如下指令:
1
2
3
|
.PHONY: install
install: manifests kustomize ## Install CRDs into the K8s cluster specified in ~/.kube/config.
$(KUSTOMIZE) build config/crd | $(KUBECTL) apply -f -
|
执行 make run 运行 controller,从 Makefile 中可以看到其实际执行了如下指令:
1
2
3
|
.PHONY: run
run: manifests generate fmt vet ## Run a controller from your host.
go run ./cmd/main.go
|
然后可以看到如下输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
...
go fmt ./...
go vet ./...
go run ./cmd/main.go
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO setup starting manager
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO controller-runtime.metrics Starting metrics server
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO starting server {"kind": "health probe", "addr": "[::]:8081"}
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO controller-runtime.metrics Serving metrics server {"bindAddress": ":8080", "secure": false}
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO Starting EventSource {"controller": "foo", "controllerGroup": "mygroup.mytest.domain", "controllerKind": "Foo", "source": "kind source: *v1.Foo"}
2023-12-19T15:14:18+08:00 INFO Starting Controller {"controller": "foo", "controllerGroup": "mygroup.mytest.domain", "controllerKind": "Foo"}
2023-12-19T15:14:19+08:00 INFO Starting workers {"controller": "foo", "controllerGroup": "mygroup.mytest.domain", "controllerKind": "Foo", "worker count": 1}
|
我们提交一个 foo.yaml 试试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: "mygroup.mytest.domain/v1"
kind: Foo
metadata:
name: test-foo
spec:
image: test-image
msg: test-message
|
执行 kubectl apply -f foo.yaml 之后我们就会在 controller 的输出中看到 foo 被打印了出来:
1
|
2023-12-19T15:16:00+08:00 INFO Received Foo {"controller": "foo", "controllerGroup": "mygroup.mytest.domain", "controllerKind": "Foo", "Foo": {"name":"test-foo","namespace":"aries"}, "namespace": "aries", "name": "test-foo", "reconcileID": "8dfd629e-3081-4d40-8fc6-bcc3e81bbb39", "Image": "test-image", "Msg": "test-message"}
|
这就是使用 kubebuilder 的一个简单示例。
总结
Kubernetes 的 CRD 和 Operator 机制为用户提供了强大的扩展性。CRD 允许用户自定义资源,而 Operators 则可以管理这些资源。正是这种扩展机制为 Kubernetes 生态系统提供了极大的灵活性和可塑性,使得它可以更广泛的应用于各种场景中。
参考资料: